Differences between SD Card, MiniSD, and MicroSD
Memory cards are essential components for smartphone or tablet users, helping to expand the often limited internal storage of these devices. Among the various types available, SD memory cards are the most widely used, including SD, MiniSD, and MicroSD variants.
The term SD stands for Secure Digital, a small form-factor flash memory designed to offer high storage capacity in a compact size. These cards are considered "secure" due to the incorporation of Content Protection for Recordable Media (CPRM) which helps prevent piracy, and a Write-Protect tab that safeguards against accidental data deletion.
SD memory cards come in various forms, primarily differing in size and capacity.
Differences Based on Size
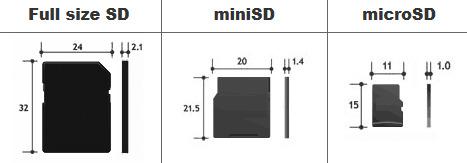
The main difference between SD Card, MiniSD, and MicroSD Card lies in their sizes. These memory cards come in three sizes: SD card, MiniSD card, and MicroSD card.
The SD card is the largest, measuring 24 x 32 mm with a thickness of 2.1 mm. It has been available since 1999. Next is the MiniSD card, which is slightly smaller at 20 x 21.5 mm and 1.4 mm thick. Introduced in 2003, MiniSD cards were commonly used in older cell phones.
The smallest and lightest is the MicroSD card, with dimensions of 11 x 15 mm and a slim 1 mm thickness. It was introduced in 2005.
Both MiniSD and MicroSD cards can fit into standard SD card slots if you use an adapter. Here’s a quick look at the dimensions and weights of these memory cards:
- MicroSD: 11mm long, 15mm wide, 1mm thick, weighs 0.5 grams
- MiniSD: 21.5mm long, 20mm wide, 1.4mm thick, weighs 1 gram
- SD Card: 32mm long, 24mm wide, 2.1mm thick, weighs 2 grams
Differences Based on Capacity

Memory cards come in various capacities, categorized into SDSC, SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC, each suited for different storage needs.
- SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity)
Commonly known as just 'SD,' these cards range from 1 MB to 2 GB, formatted with FAT16. Occasionally, you might come across SDSC cards up to 4 GB, but these are not typical and exceed the standard range for SDSC.
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity)
Introduced in 2007, SDHC is an advancement over the standard SD card, supporting capacities from 4 GB to 32 GB. These cards use the FAT32 format to enhance speed and performance. However, they require devices compatible with the SDHC format, though these devices will also support SDSC cards.
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity)
Starting at 64 GB and potentially reaching up to 2 TB, SDXC cards debuted in 2009. They are popular in smartphones and digital cameras, ideal for storing large quantities of games and applications due to their high capacity.
- SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity)
For users needing even more storage, SDUC cards offer capacities from 2 TB to an impressive 128 TB. These are excellent for extensive data storage needs, like backing up laptop data.
It's important to note that the physical size of the card does not affect its capacity. Always ensure your device is compatible with the card format you choose to fully utilize its capabilities.
Differences Based on Speed

When talking about SD cards, one of the key differences lies in their speed. This speed refers to how quickly data can be read from or written to the card.
For devices that constantly need to write data, like video recorders and drones, having an SD card with a low speed can cause the device to lag or not work as well.
For example, a high-definition camcorder needs an SD card with at least a Class 6 rating to ensure smooth video quality. Similarly, if a digital camera uses a low-speed SD card, it might take longer to capture multiple photos in a row.
Identifying the class of an SD card is easy. Just look for a circle with the letter "C" on the card, and inside that circle is a number indicating its class. Here’s a quick breakdown of the different classes:
- Class 0: No specific minimum transfer rate
- Class 2: At least 2 MB/s
- Class 4: At least 4 MB/s
- Class 6: At least 6 MB/s
- Class 10: At least 10 MB/s
Nowadays, SD card speed isn’t only about these basic classes. There are also UHS Speed Classes and Video Speed Classes, which offer even faster data transfer rates.
- UHS Speed Class 1: At least 10 MB/s
- UHS Speed Class 3: At least 30 MB/s
- Video Speed Class 6: At least 6 MB/s
- Video Speed Class 10: At least 10 MB/s
- Video Speed Class 30: At least 30 MB/s
- Video Speed Class 60: At least 60 MB/s
- Video Speed Class 90: At least 90 MB/s
Video Speed Class is a newer option designed for high-quality video recording, so you’ll often find these in cameras, drones, and similar devices.
To sum it up, the differences between SD, Mini SD, and Micro SD cards boil down to their size, capacity, and speed class. However, remember that a card’s size doesn’t affect its capacity or speed. The best way to choose a memory card is by checking its speed class and deciding what works best for your needs.
