10 Most Used PC Operating Systems in The World
A Personal Computer (PC) or laptop would not function without an embedded operating system. This operating system is a software suite loaded with programs designed to manage the system within a computing device.
The operating system is often tailored to the hardware released by the respective company. Various companies offer an array of operating systems. Our team at Carisinyal has compiled a list of these commonly used operating systems for personal computers. Here's the compilation.
1. Microsoft Windows
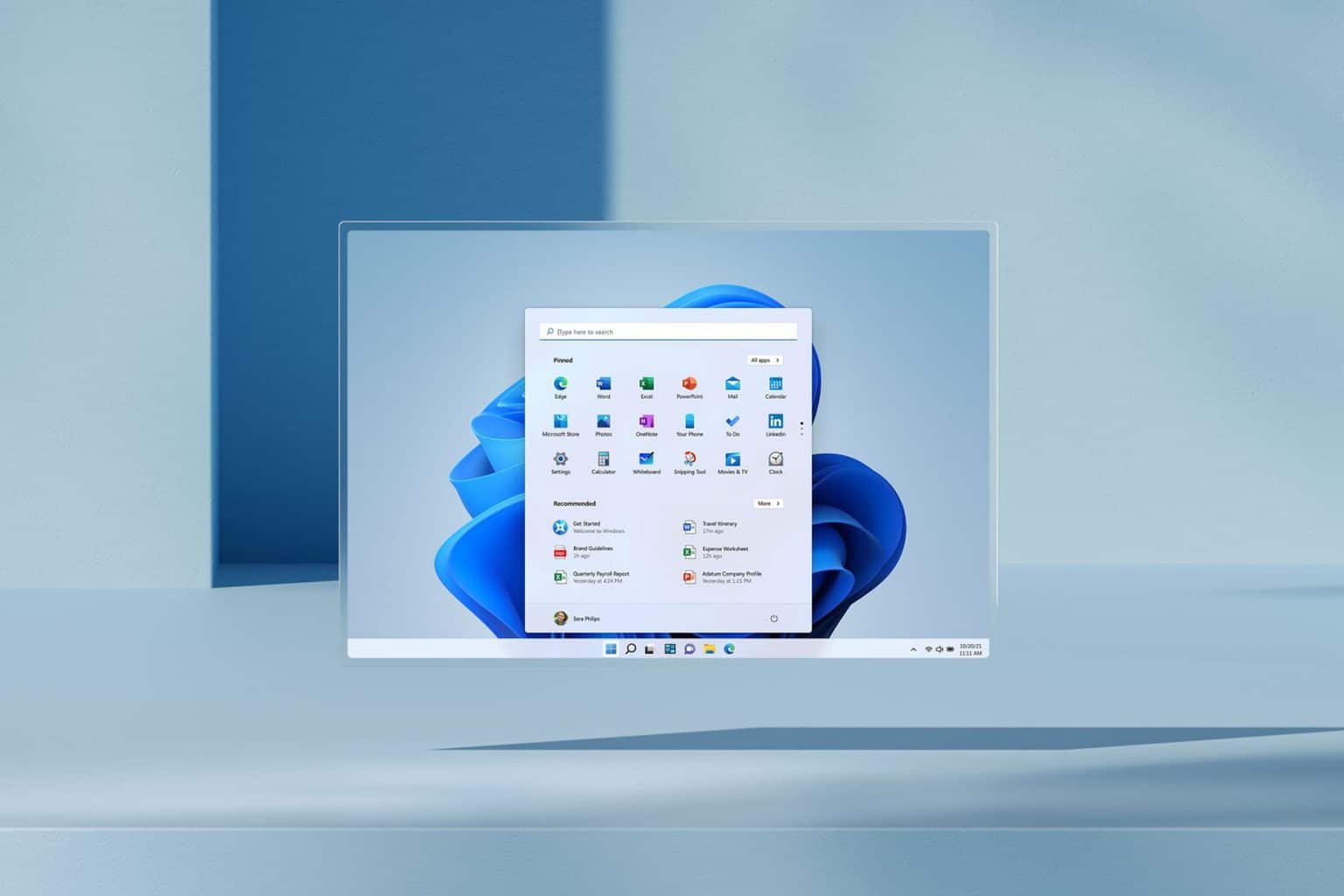
Microsoft Windows, often referred to as Windows, is an incredibly popular operating system that enjoys significant global dominance. Developed by Microsoft, Windows uses a graphical user interface as its foundation.
Ever since its initial launch, Windows has gained immense popularity, in part due to the complete set of applications provided by Microsoft, such as Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Word. Over the years, Microsoft has released numerous updated, feature-rich and modernized versions of Windows.
The very first version of Windows that hit the market was Windows 1.0, unveiled on November 20, 1985. As the years passed, Windows continued to gain traction and eventually established itself as the world's most popular operating system. As of the time this article was written, the latest version of Windows is Windows 11.
Moreover, Microsoft has introduced a cloud-based computing service known as Windows 365. This service provides cross-platform access, implying its compatibility with devices like Android and iOS phones.
Windows 365 operates within a web browser, eliminating the need for users to download any applications from the Google Play Store or the App Store to access them.
2. Mac OS
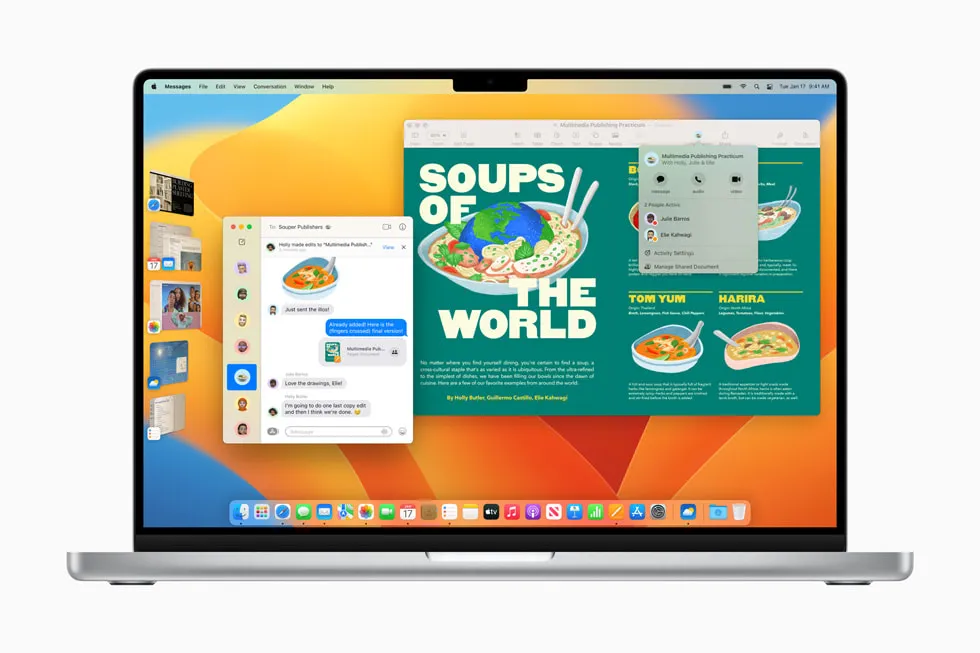
Mac OS, or Macintosh Operating System, pioneered the Graphical User Interface (GUI) based operating systems when it was first released by Apple Computer in 1984. Apple, a company known for its cutting-edge and exclusive technology, developed Mac OS specifically for its hardware.
The Mac OS presents a unique experience compared to other operating systems, especially because it doesn't feature a command line interface like its competitors.
Furthermore, Mac OS holds the distinction of being the first operating system to introduce a hierarchical file system, a feature later seen in Linux.
3. Chrome OS

Chrome OS is a relatively recent addition to the world of operating systems, having been launched in the mid-2000s. Built on a Linux foundation, Chrome OS operates primarily through web applications.
Created by Google Inc., Chrome OS can exclusively be run on hardware specifically designed by Google: Chromebooks. These devices are also released by several popular brands, including Dell, ASUS, and Acer.
The user-friendly nature of Chrome OS, coupled with its integration with Google services like Google Drive and Google Docs, makes it a popular choice. Chromebooks running Chrome OS are ideally suited for students and professionals engaging in light tasks. In terms of cost, Chromebooks are typically more affordable than conventional computers or laptops.
4. UNIX
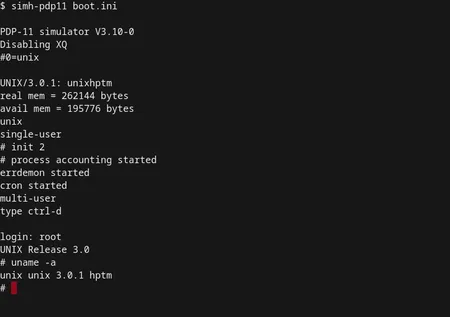
UNIX, an operating system created in 1965 as part of the Multiplexed Information and Computing Service (Multics) project, underwent significant revisions in the 1970s when Dennis Ritchie rewrote it using the C programming language.
AT&T Bell Laboratories took the helm of further UNIX development, ultimately leading to the creation of a commercial version of the operating system, named UNIX System V.
Commonly employed to manage computer networks, UNIX originally functioned as a command-line interface operating system, similar to MS-DOS. In order to improve user-friendliness, a Graphical User Interface (GUI) version of UNIX was later introduced.
5. Linux

Linux is the development of a more complete UNIX operating system. One of the key features of Linux is its open-source nature, allowing users to freely modify or replicate its programs under the official license from GNU (GNU's Not UNIX).
In 1991, a Finnish student named Linus Torvalds initially developed Linux. The operating system has found widespread use in various domains such as computer networking, software development, and other computing tasks.
In terms of cost, Linux presents a more affordable alternative than other commercial operating systems, making it an attractive choice for many users.
6. Amiga OS
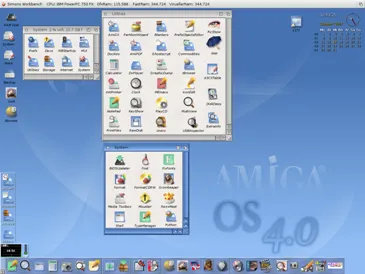
Amiga OS is an operating system with a long history, having been introduced in 1984 by Commodore International. Despite its longevity, Amiga OS hasn't achieved the same level of popularity as some other operating systems.
However, it is well-regarded for its excellent performance in handling multimedia activities. The operating system was specifically engineered to operate on Power PC-based hardware produced by Amiga.
Today, the legacy of Amiga OS is being carried forward by MorphOS. This 'successor' to Amiga OS is compatible with various computing platforms including Amiga, Mac Mini, iBook G4, and PowerBook G4.
7. Haiku
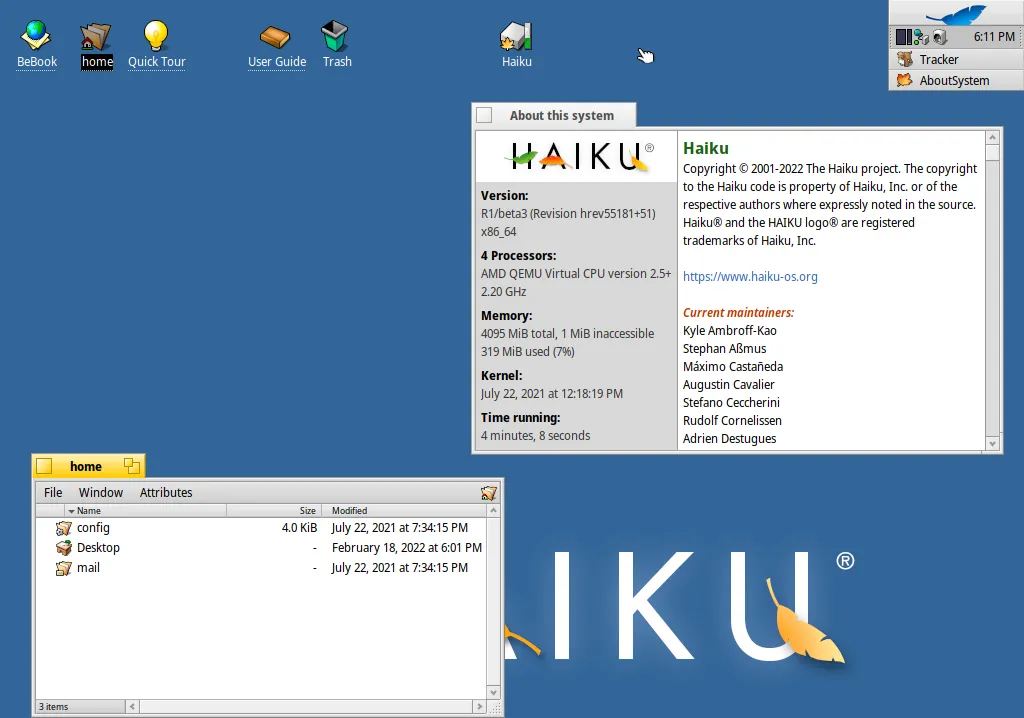
Just as MorphOS carries forward the legacy of Amiga OS, BeOS – another classic operating system – is succeeded by Haiku. According to the YouTube channel DistroTube, Haiku stands out for its uniqueness, particularly its quick installation process which takes less than 30 seconds.
Haiku brings a classic user interface that has a similarity to Windows XP. As an open-source operating system, it comes with an array of pre-installed applications, including its native browser, WebPositive.
YouTuber Dan Wood put Haiku to the test by using it to carry out a variety of tasks such as video and audio editing, and podcast creation, all executed using Haiku's built-in applications.
Despite a user interface and certain features that may seem dated, Dan Wood believes Haiku is still a viable option for everyday use.
8. AIX
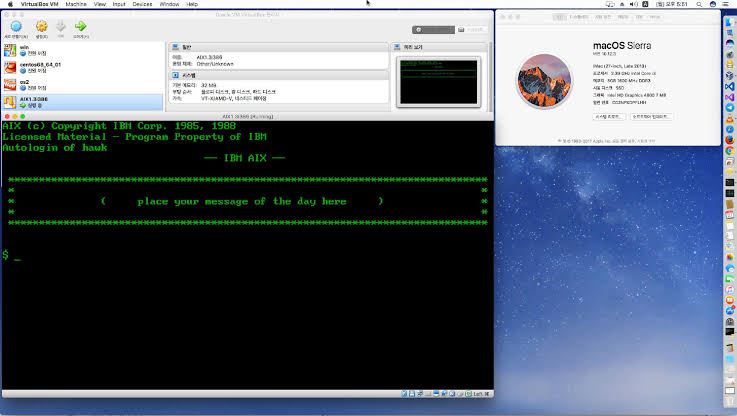
AIX, which stands for Advanced Interactive Executive, is a UNIX-based operating system developed by IBM in 1986.
Originally, this operating system was utilized as a workstation for devices equipped with RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) CPUs. Its development at the time was codenamed ROMP, an acronym for Research Office Products Division Multi Processor.
In the first version, AIX was already capable of supporting virtualization processes and high-resolution screens, thereby enhancing the user interface. The most recent version of the AIX operating system released by IBM is AIX 7.3 TL1.
9. Oracle Solaris
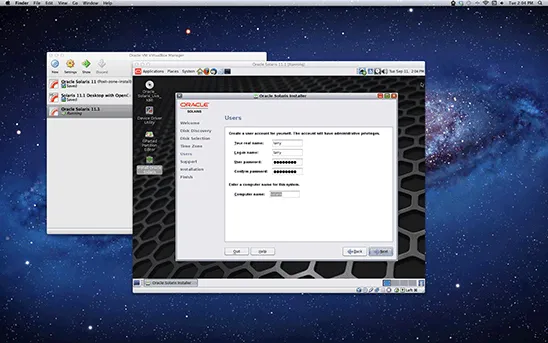
Oracle Solaris is an operating system originally developed by Sun MicroSystem in 1992 and was initially known as Sun Solaris.
The name transitioned to Oracle Solaris after Sun MicroSystem was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2010.
As an evolution of the UNIX operating system, Oracle Solaris is an open-source platform that's integrated with machines using SPARC processors. It has supported 64-bit SPARC applications since the release of Solaris 7.
10. MS-DOS
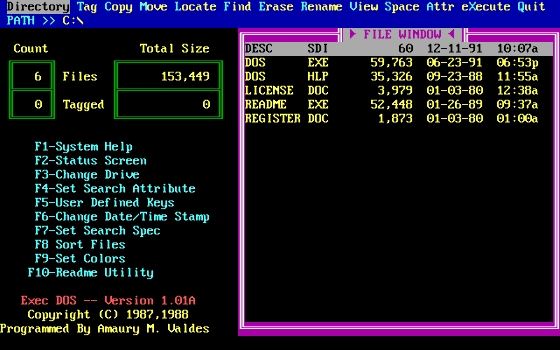
MS-DOS, the forerunner of the Microsoft Windows we use today, was an operating system frequently employed by IBM-PC computers and similar devices.
This operating system was first developed in 1981 by Bill Gates & Paul Allen and operated as a single-tasking system, primarily using Text and Command-Line modes.
With the introduction of graphical interface-based operating systems, which we now recognize as Microsoft Windows, MS-DOS began to be abandoned by its owner. Microsoft officially discontinued MS-DOS in 2000.
That concludes the list of personal computer operating systems compiled by the Carisinyal team. Some of these operating systems continue to receive updates and developments, while others, like MS-DOS, have been discontinued. So, which of these operating systems have you had experience with?
