7 Differences Between SSD and HDD You Should Know
When it comes to storage in modern computers and laptops, two main types are commonly used: SSDs (Solid State Drives) and HDDs (Hard Disk Drives). Both are widely available, with prices varying depending on their storage capacity.
As computers continue to evolve and the demand for faster performance grows, many users have made the switch to SSDs. However, HDDs are still a popular choice for those who need larger storage at a lower cost. In fact, some people opt for a combination of both.
Are you still deciding between an SSD or an HDD? Or maybe you're unsure which one suits your needs? Don’t worry – we’ll break down the differences between these two storage options so you can make an informed decision.
1. How They Work
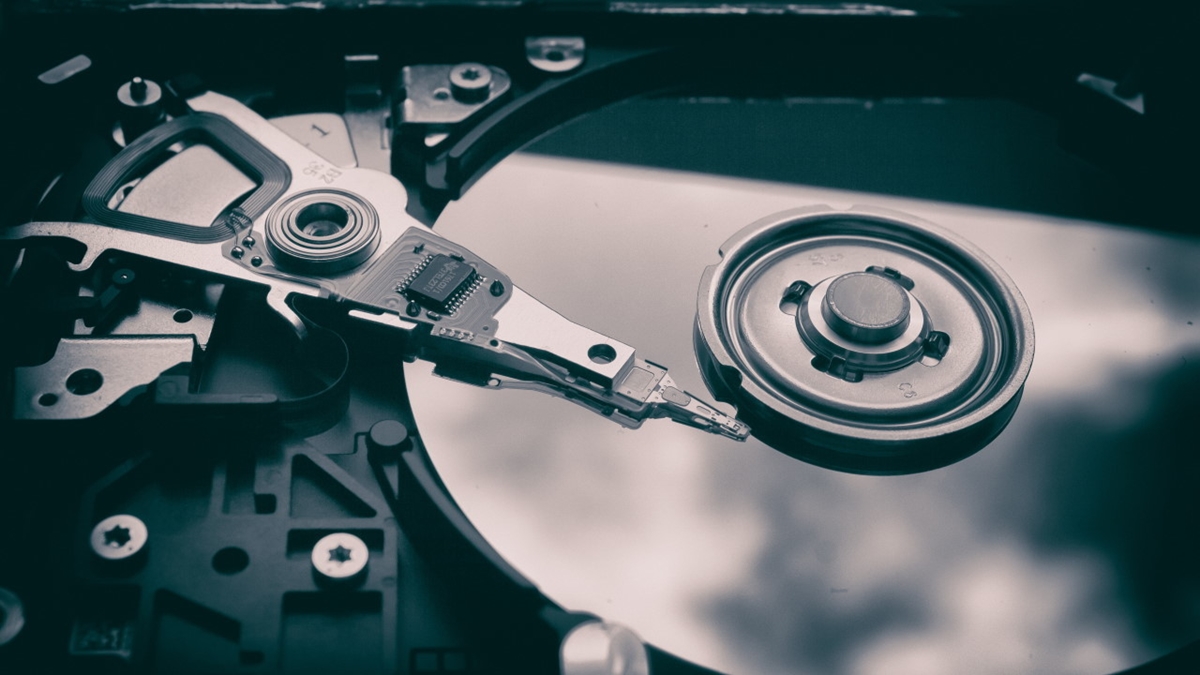

HDDs operate on a mechanical system where data is stored on magnetic disks that spin at high speeds. A read-write head physically moves over the disk to access or write data. Because of this mechanical process, HDDs tend to have slower data access times.
In contrast, SSDs use flash memory technology that consists of electronic chips with no moving parts. This means SSDs can access data much faster because there’s no need for physical movement, leading to quicker performance overall.
2. Speed
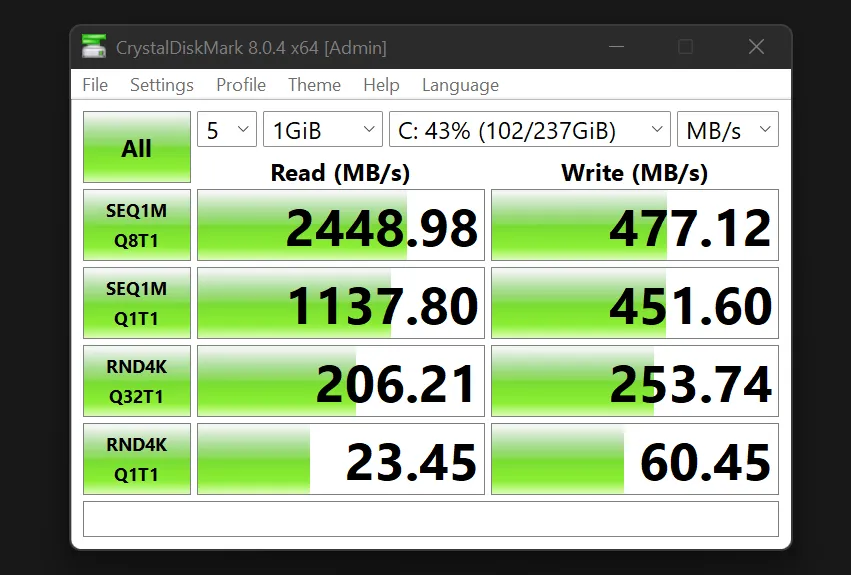
When it comes to speed, SSDs outperform HDDs by a wide margin. For instance, an SSD can boot up an operating system in a matter of seconds. It also opens applications instantly and transfers large amounts of data smoothly and efficiently.
On the other hand, HDDs take longer for these tasks due to their mechanical limitations. A typical HDD has a read/write speed of about 150 MB/s, while a 2.5-inch SATA SSD can reach speeds of around 500 MB/s.
3. Durability

HDDs have moving parts like disks and read-write heads, which makes them vulnerable to damage from impacts or shocks, especially when they're powered on.
The lifespan of an HDD depends on the condition of its magnetic disks and other mechanical components, which wear out over time. While it’s hard to predict an exact timeframe, an HDD’s performance will gradually decline with continued use.
In contrast, SSDs are more durable because they don’t have any moving parts. This makes them more resistant to shocks and impacts, which is why they’re ideal for portable devices like laptops and tablets that are frequently moved around.
SSDs do have a limit to the number of read-write cycles they can handle, but the number is high enough that they last longer than HDDs.
4. Fragmentation
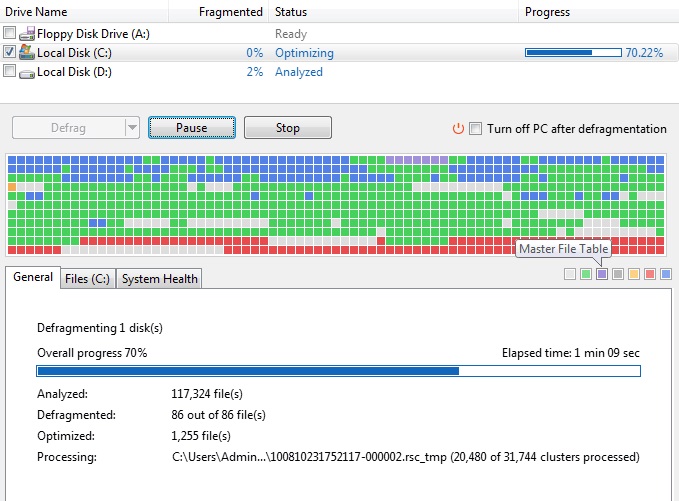
HDDs store data on solid disks divided into blocks. These blocks go through a cycle of being written to and deleted from, which can lead to fragmentation over time.
When you save data, it fills in the empty blocks first, leaving gaps behind. This causes performance issues as the system has to search for these scattered pieces of data. Defragmenting the HDD organizes these blocks to improve speed.
SSDs don’t work the same way, so fragmentation isn’t an issue. In fact, running defragmentation software on an SSD can harm its performance. Using tools like Defrag or Ultradefrag on an SSD may actually decrease its lifespan.
5. Energy Consumption and Noise Level
HDDs consume more power because they need to move the disk and read-write head. This extra power use also generates more heat and noise during operation.
In comparison, SSDs are much more energy-efficient. They don’t generate heat, and they operate quietly, making them more comfortable to use in any environment, whether it’s at work or home.
6. Form Factor
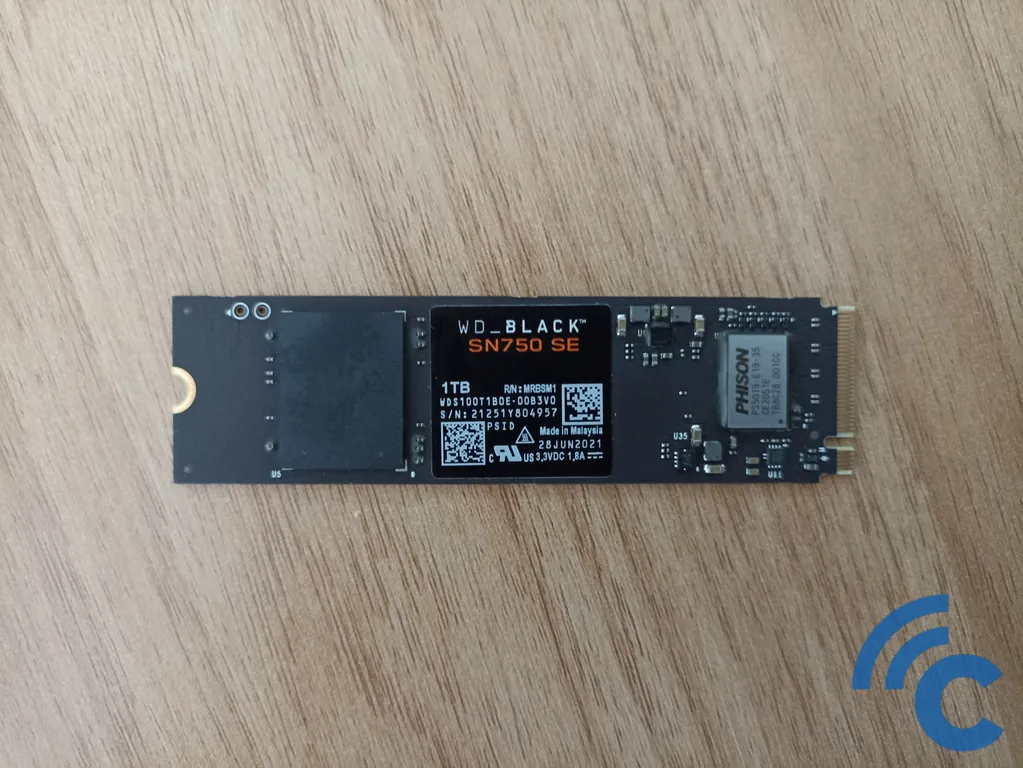

SSDs come in different shapes and sizes, with various interfaces. Some look like 2.5-inch HDDs, while others are shaped like RAM chips (M.2 and M.2 NVMe). There are also SSDs with SATA interfaces and others with PCIe interfaces.
In comparison, HDDs are available only in 2.5-inch or 3.5-inch sizes with SATA interfaces. They come in two types: external and internal, with the main difference being their intended use.
7. Price

When it comes to price, HDDs are a more affordable option than SSDs, especially if you look at the cost per gigabyte of storage. So, if you're on a budget and need a lot of storage, an HDD is the more economical choice.
On the other hand, SSDs are still more expensive per unit of storage. However, many see SSDs as a worthwhile long-term investment because of their superior performance and durability over time.
That’s a breakdown of the differences between SSDs and HDDs. We hope this article helps, especially for those of you still unsure about which storage type to choose.
